ACCOUNTING WITH FURTHER FARMERS
Technical Guidelines To Plant And Fertilize Lotus For Harvesting Seed
Lotus is known as the national flower of Vietnam. Nowadays, the lotus is a beautiful symbol and brings high economic value to farmers due to its high usability from the flowers, leaves to stems, seeds, and roots.
In this article, let’s learn about effective techniques for growing and caring for lotus seeds with Viet Nga.
Currently, in Vietnam, many different types of lotus seeds are selected/created from domestic or imported from around the world. However, they are divided into the following main groups:
– Lotus for harvesting tubers
– Lotus for harvesting flowers
– Lotus for harvesting seeds
– Lotus for decoration
Farmers can choose suitable lotus seeds based on soil, region, and investment. Depending on each type/group of lotus, there are different growth and blooming characteristics, so the technical process for planting and caring is also different.
The technical process below is for harvesting seed group lotus.
1. CHOOSING SEEDLINGS, PLANTING PROCESS
There are two common varieties of lotus plants:
– The seed-harvesting variety has a larger stem, leaves, flowers, and seed pods with deep pink flowers. It is commonly known as “Sen Trau” by the locals.
– The leaf-harvesting variety has smaller stems, leaves, flowers, and seed pods with pale pink flowers.
Therefore, it is essential to choose a suitable variety when planting.
Control the water level in the field to be 20 – 25 cm during the initial planting period to help the plants grow roots quickly.
After about 10 days, the plants should be monitored and intercropped. Then gradually increase the water level according to the growth of the plants. It is best to ensure that the water level in the field is maintained at 40- 50cm.

2. FERTILIZING
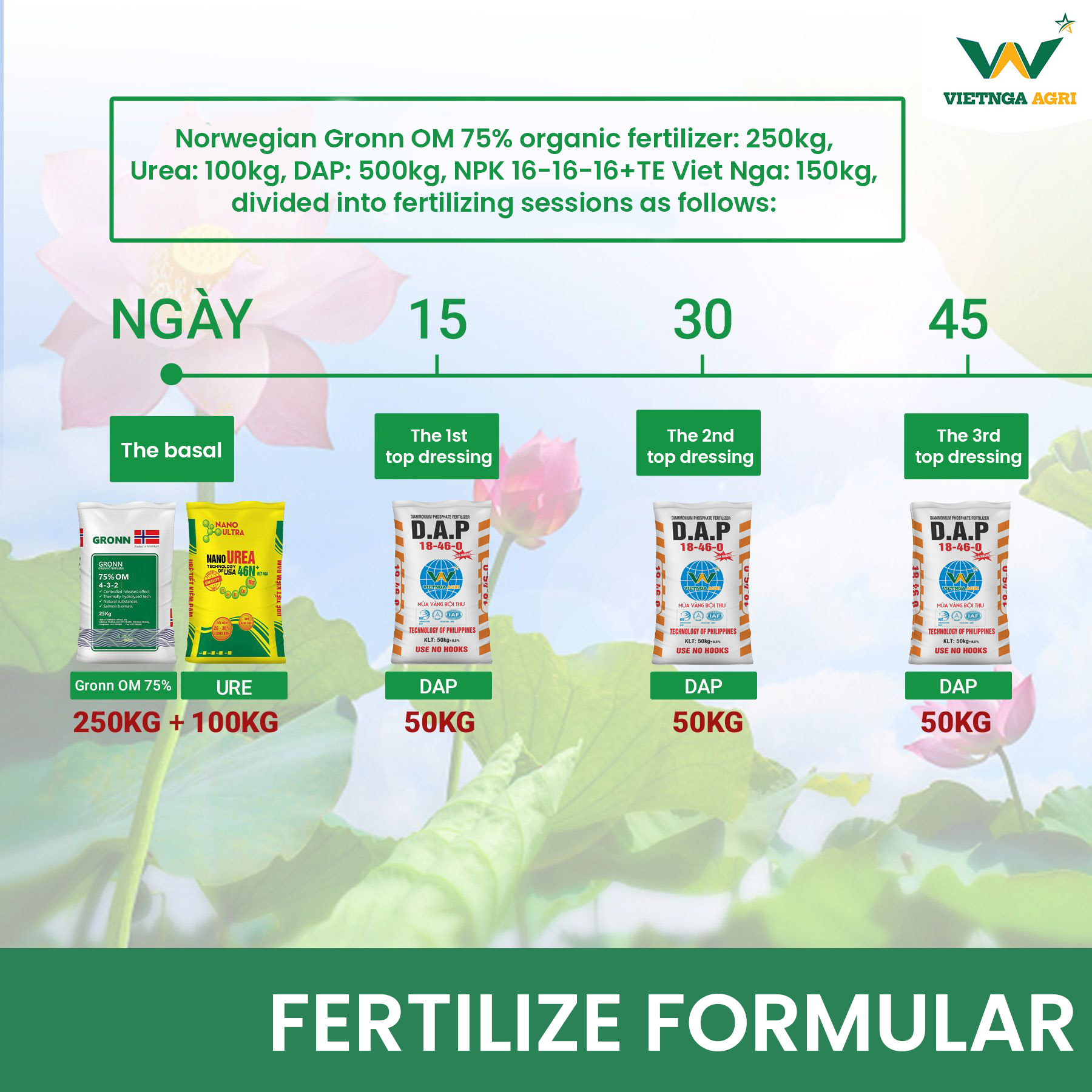
– Norwegian Gronn OM 75% organic fertilizer: 250kg, Urea: 100kg, DAP: 500kg, NPK 16-16-16+TE Viet Nga: 150kg, divided into fertilizing sessions as follows:
– Base dressing (at soil preparation stage): 250kg Norwegian Gronn OM 75% organic fertilizer + 100kg Urea
– First top dressing: 15 days after planting, 50kg DAP
– Second top dressing: 30 days after planting, 50kg DAP
– Third top dressing: 45 days after planting, 50kg DAP
– Fourth top dressing: 60 days after planting, 50kg DAP
– Fifth top dressing: 75 days after planting, 50kg DAP + 25kg NPK 16-16-16+TE Viet Nga
For subsequent sessions, apply every 15 days:
– 25kg NPK 16-16-16+TE Viet Nga + 50kg DAP until the remaining fertilizer (DAP & NPK 16-16-16+TE Viet Nga) is used up.
Note: Water needs to be changed before fertilizing, and water control is considered to be essential.
3. INSPECTION AND PREVENTION OF PLANT DISEASES AND PESTS
In the early stage and preparation for flowering, lotus is prone to red spider mites and leafhoppers. They attach themselves to the stems and flowers, sucking the sap and causing the leaves to wrinkle and wither. If the infestation is severe, it can cause the leaves to dry out, limiting growth and yield.
Chemical treatment is necessary, and Trebon 10EC can be used with a concentration of 20cc/8l of water to spray under the leaves and flowers.
In addition, lotus plants are often attacked by green worms and some other miscellaneous pests that cause severe damage to the leaves. They usually lay eggs in clusters, and newly hatched larvae concentrate on 1-2 leaves to feed on the underside of the leaf tissue, making it easy to detect during the harvest. We can kill them by hand.
If there are many leaf-eating worms, chemical treatment with Decis 2.5SC can be used following the formula 10cc/8l of water.
Note: Pesticides should be limited during the harvest period when the plants grow flowers.

4. HARVESTING
Harvesting is when black appears on the top of the seed, and the lotus stem has a pink tint. It is recommended to harvest every 2 days to avoid picking overripe lotus (which can be challenging to use) because lotus becomes overripe quickly.
When harvesting lotus seed, it is recommended to remove the leaves at the exact location as the stem and flowers (lotus plants have a characteristic where a stem with a leaf will have a stem with flowers) to help the plant continue to grow as these leaves become ineffective after the lotus is harvested. If they continue to grow, they compete for sunlight and nutrients with other leaves, especially in areas that affect future productivity.